If a residence uses well water, it is recommended that radon in the air be tested on every occupied floor of the house.
Why?
Radon is a gas that dissolves in water. If your well water has a high radon content from contact with rock that is high in radon, the water you use for domestic activities can contribute to increased radon levels in the air. When water is agitated or heated, the microscopic radon bubbles in it are released into the air.
Construction By-law
To ensure protection against radon in new buildings, the Municipality of Chelsea provides for mitigation measures in section 3.2, “Dispositions relatives à la protection contre le radon et les gaz souterrains,” of its Construction by-law.
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that comes from the decay of uranium in the Earth's crust. In the ground, it is released into the atmosphere, where it quickly dilutes, reaching concentrations too low to pose a risk.
Radon can also be present in groundwater, particularly when it flows through rocks containing uranium or radium. Deep wells may therefore have higher concentrations than surface water.
When it accumulates in an enclosed space, such as a house, radon can reach levels that are a concern for health. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations increases the risk of developing lung cancer. It is estimated that in Quebec, 10% of lung cancer deaths are associated with radon exposure.
The only way to know the radon concentration in a home is to test it.
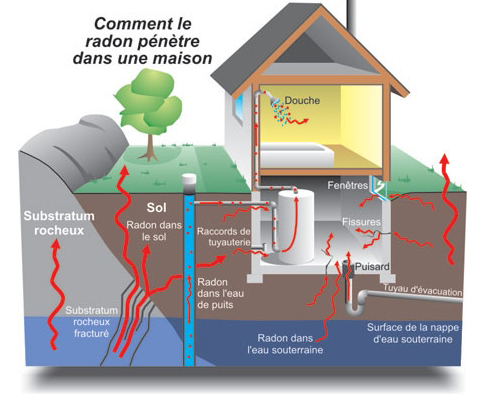
Source: Ressources naturelles Canada, 2008
Radon comes from the ground and can seep into a house through small openings in the building envelope. Once inside, it tends to accumulate in the lowest and least-ventilated areas, such as basements.
It can enter through:
- Cracks in the foundation;
- Construction joints;
- Openings around ducts and pipes;
- Crawl spaces, drains, or sumps.
Regardless of the building's age, any home can be affected. The only way to know if radon levels are of concern is to measure them with a long-term test.
Residents who wish to obtain a radon detection kit can do so at various locations (non-exhaustive list):
- Certain hardware stores
- Association pulmonaire du Québec
- AccuStar Canada
- For a list of test providers sold online to make yourself (anglais seulement)
For a list of professionals who are certified to test or mitigate your radon, you can search for a professional on the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (C-NRPP) website. This certification program is recognized by Health Canada and Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux du Québec.
There are several techniques and treatments available to reduce radon levels in your home. The Health Canada guide provides a comprehensive overview of available mitigation methods.
Radon - Reduction Guide for Canadians
For a list of professionals who are certified to test and/or mitigate your radon, you can search for a professional on the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (C-NRPP) website. This certification program is recognized by Health Canada and Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux du Québec.
Association pulmonaire du Québec
Canadian Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists
Centre intégré de santé et de services sociaux de l’Outaouais (CISSSO) (French only)
Ministère de la Santé et des Services Sociaux du Québec : Residential radon
Heanlth Canada - Reduction Guide for Canadians
Sources
The information on this page has been taken from documents produced by Health Canada, L'Association pulmonaire du Québec and the Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux du Québec.
Information
Environment Department
This page was last updated on February 23, 2026

